
What is CBD?
Cannabis has been used for its medicinal properties for centuries. In recent years, CBD has become increasingly popular as a non-psychoactive compound with a wide range of potential therapeutic benefits.
In this blog, we will discuss what CBD is, how it works, what it is used for, and some of the challenges associated with its use.

What is CBD?
CBD is one of over 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), CBD is non-psychoactive, which means that it does not produce the "high" associated with marijuana use.
CBD, short for cannabidiol, is a natural compound found in the cannabis plant. It is one of over 100 cannabinoids present in cannabis, but unlike its cousin THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), it does not produce psychoactive effects or the "high" commonly associated with marijuana use.
CBD is believed to interact with the body's endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters that helps regulate various bodily functions such as mood, appetite, pain sensation, and sleep.
Specifically, CBD is thought to bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors in the body, which can help regulate inflammation, reduce anxiety, and improve mood.
CBD is typically extracted from hemp, a variety of cannabis that contains very low levels of THC (0.3% or less). It can be consumed in a variety of forms, including oils, capsules, edibles, topicals, and more.
CBD has been the subject of much research in recent years, and some studies have suggested that it may have potential therapeutic benefits for conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and epilepsy, among others.
However, it is important to note that the research on CBD is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to fully understand its effects and potential uses. Additionally, the legality of CBD varies by country and state, so it is important to check local laws and regulations before using CBD products.
CBD is legally extracted from the hemp plant.
How CBD Works:
CBD works by interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is a complex network of receptors and signaling molecules that help to regulate various physiological processes.
The ECS is involved in regulating pain, mood, appetite, sleep, immune function, and more. The human body produces its own cannabinoids, called endocannabinoids, which bind to cannabinoid receptors to regulate these processes.
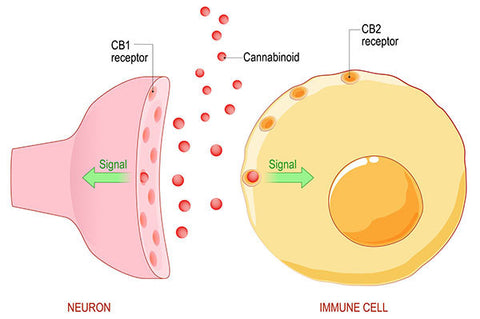
CBD interacts with the ECS by binding to cannabinoid receptors, mainly CB1 and CB2 receptors.
CB1 receptors are mainly found in the brain and central nervous system and are involved in regulating pain, mood, and appetite. CB2 receptors are mainly found in the immune system and peripheral tissues and are involved in regulating inflammation and immune function.
When CBD binds to these receptors, it can have a variety of effects on the body, including reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving mood.
CBD may also have neuroprotective properties, which means that it may help to protect the brain from damage and improve cognitive function.
What is CBD Used For?
It's important to note that the FDA has not approved the use of CBD for the below uses. The only FDA approved CBD drug is Epidiolex, which has been proven to significantly reduce seizures in people living with LGS, Dravet syndrome, or TSC for whom multiple previous antiseizure medicines did not work well.
CBD has a wide range of potential therapeutic applications, and it has been studied for its effects on various conditions, including:
Pain: CBD has been shown to have pain-relieving properties and may be effective in treating chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, neuropathic pain, and more.
CBD may work by reducing inflammation and altering pain perception.

Anxiety and Depression: CBD may have anxiolytic and antidepressant properties and has been studied for its potential to treat anxiety and depression.
CBD may work by interacting with serotonin receptors in the brain, which are involved in regulating mood.
Epilepsy: CBD has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of certain forms of epilepsy, including Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
CBD may work by reducing the frequency and severity of seizures.
Cancer: CBD has been studied for its potential to help reduce cancer-related symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting, and it may also have anti-tumor properties.
CBD may work by inhibiting cancer cell growth and promoting cancer cell death.
Neurological Disorders: CBD may have neuroprotective properties and has been studied for its potential to treat a wide range of neurological conditions, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
CBD may work by reducing inflammation and protecting neurons from damage.
Skin Conditions: CBD may have anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties and has been studied for its potential to treat a variety of skin conditions, including acne and psoriasis.
CBD may work by reducing inflammation and regulating sebum production in the skin.
Challenges with CBD:
While CBD has a wide range of potential therapeutic benefits, there are also some challenges associated with its use, including:

Lack of Regulation: CBD is not regulated by the FDA, which means that there is no standardized dosing or quality control for CBD products.
This can make it difficult for consumers to know what they are getting and to ensure that the product is safe and effective.
If you want to buy CBD online, always ensure the product comes with third party lab results, so that you know exactly what you are getting.
Drug Interactions: CBD may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, anti-seizure medications, and others.
This can lead to potential side effects or reduced effectiveness of the medication.
Side Effects: While CBD is generally considered safe, it can cause side effects in some people, including dry mouth, drowsiness, and changes in appetite.
In rare cases, CBD may also cause liver damage, particularly in people who are taking high doses of the compound.
Legal Status: The legal status of CBD can be confusing, as it varies from state to state and country to country. In some places, CBD is legal for medical use but not for recreational use, while in others, it is legal for both.

This can make it difficult for consumers to know whether they are allowed to use CBD products in their area.
Lack of Research: While there have been many studies on the potential therapeutic benefits of CBD, there is still a lack of research in certain areas.
For example, more research is needed to determine the long-term effects of CBD use, as well as its effects on children and pregnant women.
Quality Control: Due to the lack of regulation of CBD products, there can be inconsistencies in the quality and potency of CBD products.
This can lead to ineffective products, or even harmful products if they contain contaminants or dangerous additives.
Mislabeling: Another issue with CBD products is mislabeling. Some products may claim to contain a certain amount of CBD but actually contain less, or they may contain other cannabinoids or additives not listed on the label.
This can be particularly dangerous for people with certain medical conditions or allergies.
Stigma: While the stigma around cannabis is gradually diminishing, there are still some people who view CBD as a drug and are hesitant to try it.
This stigma can make it difficult for people to access CBD products, particularly in countries or states where cannabis is not legal.
Dosage: CBD dosages can be difficult to determine, as there is no standardized dosing for CBD products.
This can make it difficult for consumers to know how much CBD they are actually getting and to determine the optimal dosage for their specific needs.
Price: CBD products can be expensive, particularly if they are high quality and derived from organic hemp.

This can make it difficult for some people to afford CBD products, particularly those who may benefit the most from them.
Despite these challenges, the potential therapeutic benefits of CBD are numerous and significant. Some of the potential uses of CBD include:
Pain Relief: CBD may help to alleviate chronic pain by reducing inflammation and affecting the way that the brain perceives pain signals.
Anxiety and Depression: CBD may have anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects, making it a potential treatment option for people with anxiety or depression.
Neurological Disorders: CBD may help to reduce seizures in people with epilepsy, and it may also have potential benefits for people with Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological disorders.
Cancer: CBD may have anti-cancer properties and may be useful in the treatment of certain types of cancer.
Skin Disorders: CBD may help to reduce inflammation and irritation in people with skin disorders such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
Addiction: CBD may help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in people with substance use disorders, making it a potential treatment option for addiction.

In conclusion, CBD is a promising compound with numerous potential therapeutic benefits. While there are challenges associated with its use, including the lack of regulation, drug interactions, side effects, legal status, and the need for more research, the potential benefits of CBD make it a promising treatment option for a wide range of medical conditions.
As research into the effects of CBD continues, it is likely that we will learn more about the potential benefits of this compound and how it can best be used to improve health and well-being.
